Reflective, high-visibility clothes could stand out to human drivers at night time, however a current examine suggests it could be invisible to a car’s automated crash prevention know-how.
The examine, carried out by the Insurance coverage Institute for Freeway Security (IIHS) within the US, got down to decide the effectiveness of autonomous emergency braking (AEB) programs detecting pedestrians sporting reflective clothes at night time.
Whereas IIHS analysis up to now has proven AEB programs cut back the speed of pedestrian-related incidents of all severities by 27 per cent, the security system’s night-time limitations are described as “a significant issue”, as most deadly pedestrian crashes happen at night time.
In response to the IIHS, automakers are working to deal with such points, although the non-profit organisation aimed to additional examine “the results of conspicuous clothes and elevated roadway lighting” on the efficiency of pedestrian AEB programs with its newest analysis.
100s of recent automobile offers can be found via CarExpert proper now. Get the consultants in your facet and rating an important deal. Browse now.
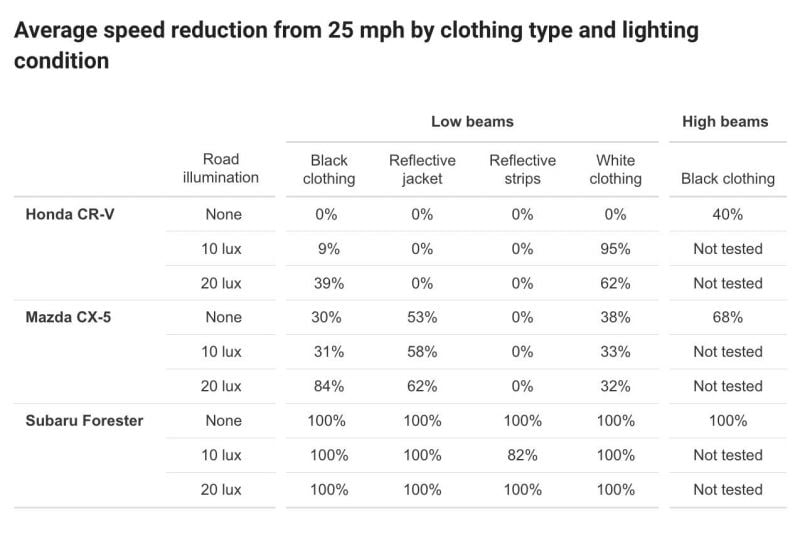
As a part of the examine, the IIHS gathered three 2023 vehicles – a Honda CR-V, Mazda CX-5, and Subaru Forester – that are all fitted with pedestrian AEB programs.
A number of trials had been subsequently carried out with an adult-sized dummy wearing all black; all white; black pants with a completely reflective jacket; and all black with reflective strips – the latter of which supposed to imitate outfits worn by street building staff however with out the everyday vibrant yellow or orange.
The dummy would then traverse a pedestrian crossing in three totally different roadway lighting eventualities. One featured no roadway lighting in any respect, one other at 10 lux (twilight), and the ultimate at 20 lux (the authorized requirement for crossings within the US).
All three automobiles approached the crossing at 25mp/h (40.2km/h).
When the dummy was wearing black, each the CR-V and CX-5 slowed considerably when utilizing their high-beams with no street illumination. In the identical lighting situations however utilizing low-beam lights, the CR-V did not sluggish in any respect, and the CX-5 diminished its pace by lower than one-third. Each automobiles carried out higher with 20 lux of further mild.
The Honda couldn’t detect the dummy when it was wearing white with no street illumination, however improved within the 10 and 20 lux eventualities. Each vehicles started to wrestle considerably when reflective clothes was launched.
“When the dummy was dressed within the reflective jacket, the CR-V didn’t sluggish in any of the trials, no matter further roadway lighting,” the IIHS wrote in its launch
“In distinction, with no roadway illumination and with 10 lux of added mild, the CX-5 slowed far more than it did when the dummy was clad in black. However with 20 lux of added mild, it carried out worse with the dummy within the reflective jacket than when it was sporting the black outfit.”
When the dummy was adorned with reflective strips, each the Honda and Mazda did not sluggish in all lighting eventualities.
“The location and movement of reflective strips on the joints and limbs of pants and jackets permits drivers to rapidly recognise the sample of motion as an individual,” IIHS senior analysis scientist and examine writer David Kidd mentioned.
“Sadly, the shifting strips didn’t have the identical impact for the pedestrian AEB programs we examined and possibly confounded their sensors.”
The IIHS says “it’s not clear” why the CR-V and CX-5 struggled with the dummy’s reflective strips or what number of different producers’ programs additionally face the identical limitiations.
As for the Forester, which was fitted with Subaru’s established EyeSight security know-how, it got here to an entire cease in each trial besides one, during which the dummy was sporting reflective strips and the roadway was illuminated to 10 lux.
Even in that check, the IIHS stories it slowed by “greater than 80 per cent”.
The IIHS suggests additional analysis is required to completely perceive how crash avoidance programs reply to the clothes worn by street building crews and emergency staff, whereas organisation president David Harkey described the shortcomings as a “worrisome blind spot”.
“These outcomes recommend that some automakers have to tweak their pedestrian automated emergency braking programs,” Mr Harkey mentioned.
“It’s untenable that the garments that pedestrians, cyclists and roadway staff put on to be secure could make them tougher for crash avoidance know-how to recognise.”
It’s not the primary time points with pedestrian AEB know-how have been reported.
Basic Motors (GM) was in scorching water for an incident during which one in all its Cruiser autonomous robo-taxis hit a pedestrian, after which the corporate admitted to many crucial failings.
MORE: GM’s driverless automobile division admits failings after pedestrian collision